10.3 Connecting to BETYdb on the VM via SSH
Sometimes, you may want to develop code locally but connect to an instance of BETYdb on the VM.
To do this, first open a new terminal and connect to the VM while enabling port forwarding (with the -L flag) and setting the port number. Using 5433 does not conflict with the postgres default port of 5432, the forwarded port will not conflict with a postgres database server running locally.
ssh -L 5433:localhost:5432 carya@localhost:6422This makes port 5433 on the local machine match port 5432 on the VM.
This means that connecting to localhost:5433 will give you access to BETYdb on the VM.
To test this on the command line, try the following command, which, if successful, will drop you into the psql console.
psql -d bety -U bety -h localhost -p 5433To test this in R, open a Postgres using the analogous parameters:
library(DBI)
library(RPostgres)
con <- dbConnect(
drv = Postgres(),
user = "bety",
password = "bety",
dbname = "bety",
host = "localhost",
port = 5433
)
dbListTables(con) # This should return a vector of bety tablesNote that the same general approach will work on any BETYdb server where port forwarding is enabled, but it requires ssh access.
10.3.1 Using Amazon Web Services for a VM (AWS)
Login to Amazon Web Services (AWS) and select the EC2 Dashboard. If this is your first time using AWS you will need to set up an account before you are able to access the EC2 Dashboard. Important: You will need a credit card number and access to a phone to be able to verify AWS account registration. AWS is free for one year.
- Choose AMI
- On the top right next to your name, make sure the location setting is on U.S. East (N. Virginia), not U.S. West (Oregon)
- On the left click, click on EC2 (Virtual servers), then click on “AMIs”, also on the left
- In the search window toggle to change “Owned by me” to “Public images”
- Type “pecan” into the search window
- Click on the toggle button on the left next to PEcAn1.4.6
- Click on the “Launch” button at the top
- Choose an Instance Type
- Select what type of machine you want to run. For this demo the default, t2.micro, will be adequate. Be aware that different machine types incur very different costs, from 1.3 cents/hour to over $5/hr https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/
- Select t2.micro, then click “Next: Configure Instance Details”
- Configure Instance Details
- The defaults are OK. Click “Next: Add Storage”
- Add Storage
- The defaults are OK. Click “Next: Tag Instance”
- Tag Instance
- You can name your instance if you want. Click “Next: Configure Security Group”
- Configure Security Group
- You will need to add two new rules:
- Click “Add Rule” then select “HTTP” from the pull down menu. This rule allows you to access the webserver on PEcAn.
- Click “Add Rule”, leave the pull down on “Custom TCP Rule”, and then change the Port Range from 0 to 8787. Set “Source” to Anywhere. This rule allows you to access RStudio Server on PEcAn.
- Click “Review and Launch” . You will then see this pop-up:
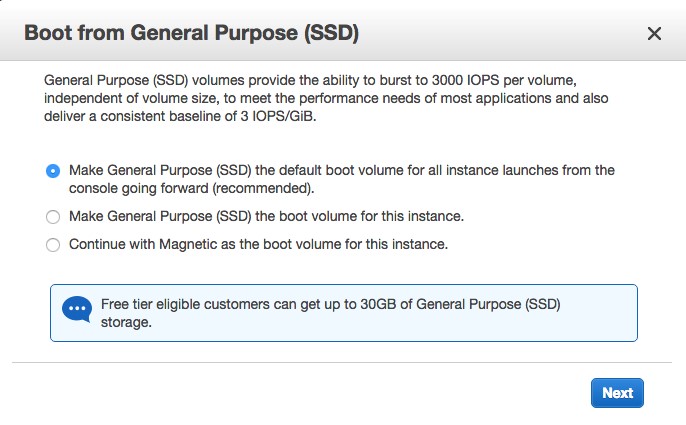
Select the default drive volume type and click Next
- Review and Launch
- Review the settings and then click “Launch”, which will pop up a select/create Key Pair window.
- Key Pair
- Select “Create a new key pair” and give it a name. You won’t actually need this key unless you need to SSH into your PEcAn server, but AWS requires you to create one. Click on “Download Key Pair” then on “Launch Instances”. Next click on “View Instances” at the bottom of the following page.
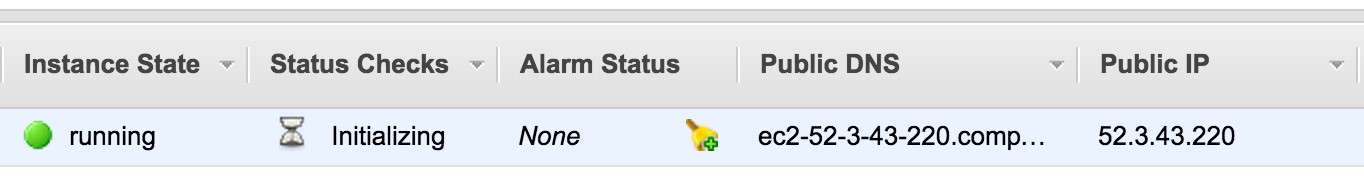
- Instances
- You will see the status of your PEcAn VM, which will take a minute to boot up. Wait until the Instance State reads “running”. The most important piece of information here is the Public IP, which is the URL you will need in order to access your PEcAn instance from within your web browser (see Demo 1 below).
- Be aware that it often takes ~1 hr for AWS instances to become fully operational, so if you get an error when you put the Public IP in you web browser, most of the time you just need to wait a bit longer. Congratulations! You just started a PEcAn server in the “cloud”!
- When you are done using PEcAn, you will want to return to the “Instances” menu to turn off your VM.
- To STOP the instance (which will turn the machine off but keep your work), select your PEcAn instance and click Actions > Instance state > Stop. Be aware that a stopped instance will still accrue a small storage cost on AWS. To restart this instance at any point in the future you do not want to repeat all the steps above, but instead you just need to select your instance and then click Actions > Instance state > Start
- To TERMINATE the instance (which will DELETE your PEcAn machine), select your instance and click Actions > Instance state > Terminate. Terminated instances will not incur costs. In most cases you will also want to go to the Volumes menu and delete the storage associated with your PEcAn VM.Remember, AWS is free for one year, but will automatically charge a fee in second year if account is not cancelled.
10.3.2 Creating a Virtual Machine
First create virtual machine
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
# CREATE VM USING FOLLOWING:
# - VM NAME = PEcAn
# - CPU = 2
# - MEMORY = 2GB
# - DISK = 100GB
# - HOSTNAME = pecan
# - FULLNAME = PEcAn Demo User
# - USERNAME = xxxxxxx
# - PASSWORD = yyyyyyy
# - PACKAGE = openssh
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------To enable tunnels run the following on the host machine:
VBoxManage modifyvm "PEcAn" --natpf1 "ssh,tcp,,6422,,22"
VBoxManage modifyvm "PEcAn" --natpf1 "www,tcp,,6480,,80"Make sure machine is up to date.
UBUNTU
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get -y dist-upgrade
sudo rebootCENTOS/REDHAT
sudo yum -y update
sudo rebootInstall compiler and other packages needed and install the tools.
UBUNTU
sudo apt-get -y install build-essential linux-headers-server dkmsCENTOS/REDHAT
sudo yum -y groupinstall "Development Tools"
sudo yum -y install wgetInstall Virtual Box additions for better integration
sudo mount /dev/cdrom /mnt
sudo /mnt/VBoxLinuxAdditions.run
sudo umount /mnt
sudo usermod -a -G vboxsf caryaFinishing up the machine
Add a message to the login:
sudo -s
export PORT=$( hostname | sed 's/pecan//' )
cat > /etc/motd << EOF
PEcAn version 1.4.3
For more information about:
Pecan - http://pecanproject.org
BETY - http://www.betydb.org
For a list of all models currently navigate [here](../users_guide/basic_users_guide/models_table.md)
You can access this system using a webbrowser at
http://<hosting machine>:${PORT}80/
or using SSH at
ssh -l carya -p ${PORT}22 <hosting machine>
where <hosting machine> is the machine where the VM runs on.
EOF
exitFinishing up
Script to clean the VM and remove as much as possible history cleanvm.sh
wget -O ~/cleanvm.sh http://isda.ncsa.uiuc.edu/~kooper/EBI/cleanvm.sh
chmod 755 ~/cleanvm.shMake sure machine has SSH keys rc.local
sudo wget -O /etc/rc.local http://isda.ncsa.illinois.edu/~kooper/EBI/rc.localChange the resolution of the console
sudo sed -i -e 's/#GRUB_GFXMODE=640x480/GRUB_GFXMODE=1024x768/' /etc/default/grub
sudo update-grubOnce all done, stop the virtual machine
history -c && ${HOME}/cleanvm.sh